
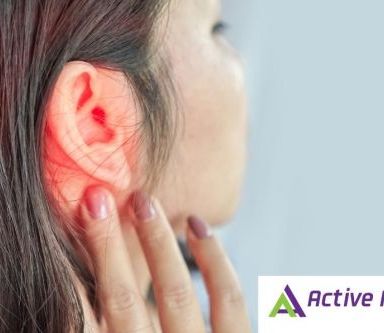
Experiencing a common cold can be a bothersome affair, with symptoms ranging from congestion to coughing. However, for some individuals, a cold may bring an unexpected companion: tinnitus from cold. Let’s delve into the phenomenon of tinnitus occurring during or after a cold, understand its possible causes and explore coping strategies for managing tinnitus symptoms in such situations.
Understanding tinnitus
Tinnitus is the perception of ringing, buzzing, humming or other phantom sounds in the absence of external stimuli. It can be temporary or chronic, and it affects millions of people worldwide. Tinnitus itself is not a condition but a symptom of an underlying issue, such as damage to the auditory system, exposure to loud noise or even certain medical conditions.
The connection: tinnitus from cold
While tinnitus is not a direct symptom of the common cold, many individuals report experiencing tinnitus during or after a cold. Several factors may contribute to the onset of tinnitus including eustachian tube dysfunction, sinus congestion and inflammation, and medications.
Eustachian tube dysfunction
The Eustachian tubes, responsible for equalizing air pressure in the middle ear, can become congested or inflamed during a cold. This dysfunction can lead to changes in pressure and fluid accumulation in the middle ear, potentially affecting the auditory system and triggering tinnitus.
Sinus congestion
Sinus congestion and inflammation associated with a cold can impact the flow of blood and oxygen to the ears, leading to changes in auditory perception and the perception of tinnitus sounds.
Medications
Over-the-counter cold medications, such as decongestants or antihistamines, can have side effects that affect the auditory system. These medications may cause dehydration or changes in blood flow, potentially contributing to tinnitus symptoms.
Coping strategies
While tinnitus caused by a cold may resolve as the underlying cold subsides, some strategies that can help alleviate tinnitus symptoms include relaxation techniques, sound therapy, self-care, avoiding triggers, seeking medical advice and rest.
Relaxation techniques
Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation or yoga, can help reduce the stress and anxiety associated with tinnitus. Relaxation techniques promote overall well-being and can have a positive impact on tinnitus perception.
Sound therapy
Masking or distracting from tinnitus sounds through sound therapy can be beneficial. Playing background noise, such as a fan, white noise machine or soothing music, can help divert attention from the tinnitus sounds and provide relief.
Avoiding triggers
Identifying and avoiding potential triggers that worsen tinnitus symptoms can be helpful. These triggers may include exposure to loud noise, excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, smoking and high-stress levels. Minimizing these factors can provide some relief from tinnitus discomfort.
Seeking medical advice
If tinnitus persists or becomes bothersome during or after a cold, consulting a healthcare professional, such as an audiologist or otolaryngologist, is recommended. They can evaluate the underlying cause, offer guidance and suggest appropriate treatment options if necessary.
Self-care and rest
Ensuring adequate rest and practicing good self-care during a cold can support the body's natural healing process. Staying hydrated, getting plenty of sleep and adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact overall well-being, potentially alleviating tinnitus symptoms.
Visit us
Experiencing tinnitus from cold can be an unwelcome addition to an already uncomfortable situation. It is important to remember that these symptoms are usually temporary and will likely resolve as the cold subsides. If tinnitus persists, you should reach out to a health professional or hearing specialist for a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate guidance. Contact us today to see how we can help!




Comments